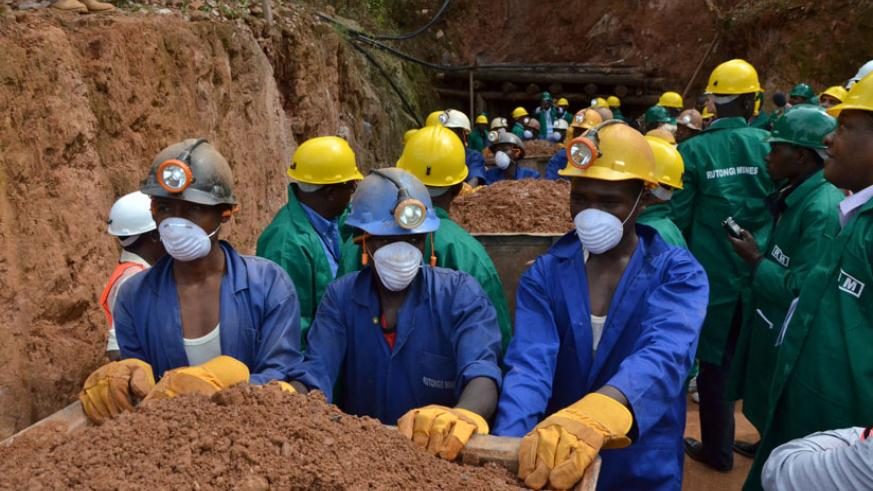
A strong, investor friendly legal and policy framework
Overview
- Mining in Rwanda presents un exploited opportunities in ores, processing and diversification
- Rwanda’s main mineral exports are ores processed to extract tin, tantalum and tungsten and few gold and gemstones
- Mining is the second largest export in the Rwandan economy. In 2017, the sector generated about $373.4 Million of foreign exchange.
- All mineral exports from Rwanda are traceable through the tagging system currently accepted by the downstream buyers of the minerals.
- Exploration works to identify and delineate more mineral deposits are underway
- A strong, investor friendly legal and policy framework has been put in place
Total investment (cumulative) in the sector will be increased from USD 150 million to USD 500 million by 2017/2018.
Key Targets
- Contribution to GDP is to increase from 1.2% to 5.27 % by 2017/2018.
- The number of working people (16 years and above) with main job in the mining sub-sector will increase from 20,000 to 60,000 by 2017/2018.
- Total investment (cumulative) in the sector will be increased from USD 150 million to USD 500 million by 2017/2018.
- Export earnings will increase from USD 158 million in 2011 to USD 400 million by 2017/2018
- Certified mine sites with efficient water and wastes management system to increase from 20% in 2011/2012 to 100% by 2017/2018
- Percentage of the certified mine sites with safe and secure working conditions will be increased from 25% in 2011/2012 to 80% by 2017/2018
Mining Investment Opportunities
Exploration Opportunities:
- The Government of Rwanda has invested in exploration works in Prospective Target Areas s to generate good primary geology data to be used by mineral exploration companies.
- Intensive, up to date and detailed mineral exploration can be carried out in the recently identified Prospective Target Areas (PTAs) to delineate and quantify their mineral resources.
Mining
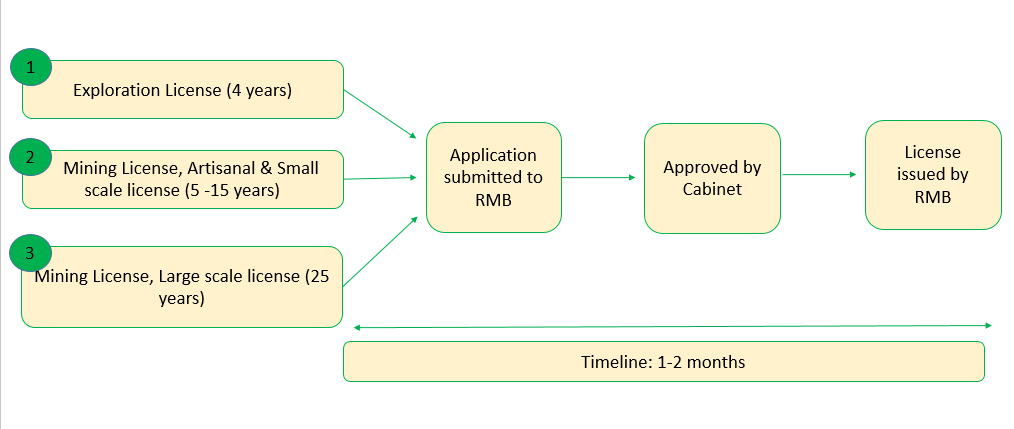
- The mining law grants the right to exploit three categories of mines: artisanal, small scale, and largescale mines to any person or company with proven technical expertise and financial capacity to develop and run a mining project.
Value Addition:
- Rwanda’s mineral ores produced in the country are exported as 100% raw mineral concentrates, not as metals.
- The establishment of processing plants to smelt cassiterite into tin, refining wolframite into tungsten, tantalite into tantalum, gemstones cutting and polishing, and gold refinery are open to private investors
Industrial Mining
- Currently, Rwanda’s mining sector is mostly artisanal;
- Modern technology is needed to upgrade the sector to a semi- mechanized and later at industrial level to increase production, which is low compared to the proven potential.
- Mining equipment including drillers, bulldozers, gravity table shakers are needed to upgrade the sector.
Gemstones:
- The exploration and exploitation of gemstones is still at a low level in Rwanda.
- The country possesses a variety of gemstones including: beryl (Aquamarine), Amblygonite,Corundum (Ruby and sapphire), Tourmalines and different types of Quartz.
- There are opportunities to set up businesses cutting and polishing gemstones.
Industrial Minerals:
- Rwanda possesses a variety of minerals such as good quality silica sands, kaolin, granite, vermiculite, diatomite, clays, limestone, talcum, gypsum and pozzolan.
- However, exploitation and processing of industrial minerals to meet the demand for construction materials is still low especially production of tiles, slabs sculptures, paints, bricks and concrete aggregates.
Mining Equipments:
Mining equipment and services are required both in the country and the region. There is a gap in companies trading in or offering mining related services.
Trade in Mineral Substances:
- Trade in mineral substances is carried out by holders of mining and mineral trading licenses and owners of smelting and screening companies.
- Trading in minerals, including cassiterite, wolframite and niobium – tantalite, must contain at least 30% value added.
Designing Policy and strategies
Regulatory frame work
- Rwanda Development Board (RDB): Investment process, guidance, facilitation, leading negotiations for strategic projects, issuing EIA, and providing incentives
- Rwanda Mines Board (RMB): Designing Policy and strategies, Issuing of Mining and Quarry licenses, laws and regulations elaboration and supervision and Promotion of mining sector at national and international levels, Enhance geological and mining knowledge of the country, improve exploitation and investment conditions, monitoring mining activities to comply with the law and increase value addition to Rwanda’s mines and quarries.
- Rwanda environment management authority (REMA): Setting environment standards, environment inspection of mining projects and rehabilitation of exhausted mines and quarries
- Ministry of Trade and Industry (MINICOM): Mineral trading license
Setting environment standards, environment inspection of mining projects
Mineral traceability in Rwanda use the ITRI/iTSCi ‘tag and bag’ scheme was initiated in late 2010
Mineral transparency initiatives in Rwanda
- Rwanda started following the enactment of the Dodd-Frank “conflict-minerals” Act
- Mineral traceability in Rwanda use the ITRI/iTSCi ‘tag and bag’ scheme was initiated in late 2010
- The Government passed a mineral anti-smuggling regulations in March 2011
- Since April 2011, 100% of Rwandan minerals are traceable from their mine sites up to their export point
- Since 2012, Rwanda has integrated the Regional Certification Mechanism (RCM) in its mining regulations
- The RCM forms part of the ICGLR Regional Initiative on Natural Resources, adopted by heads of state in December 2010
Corporate Income Tax Holiday up to 7 years for investment of at least US$ 50 m
Non Fiscal Incentives
- Facilitate quick Investment registration
- Facilitation with tax related services and exemptions
- Facilitation with obtaining visas and Work permits
- Notary services provided by Our One Stop Center
- Assigning Key Account Manager to projects registered with in the One Stop Center
- Facilitation to access utilities
Fiscal Incentives
- 0% Corporate Income Tax for Mining companies planning to relocate H/Q’s to Rwanda
- Corporate Income Tax Holiday up to 7 years for investment of at least US$ 50 m
- 15% Preferential Corporate Income tax for projects exporting processed minerals up to 50% of turnover of minerals produced in Rwanda
- Investment allowance of 50% or Accelerated depreciation of 50%
- Capital Gains tax exemption and free repatration of Capital and assets
- Import free on Heavy Machinary used in Mining
- Vat exemption on Mining equipments
Regional Certification Mechanism (RCM)
Contact Us
For any further details/information you may require, please contact:
Mr. Chris Picton Shyaka
Industrial Development Analyst
Email: chrispicton.shyaka@rdb.rw
Telephone: +250788514204
Copy to:
Philip Lucky
Head-Investmnt Promotion & Facilitation.
Email: philip.lucky@rdb.rw